GEO vs SEO: What's The Difference And Why It Matters?

Updated by
Updated on Feb 15, 2026
Learn how GEO vs SEO differ and why you need both to win in AI search and get proven strategies to optimize for AI and Google together.
SEO focuses on ranking web pages; GEO ensures your brand gets cited in AI-generated answers
Optimizing for AI search is a hot take among marketers right now.
Some insist AI search is fundamentally different: a new channel that demands dedicated strategies, fresh frameworks, and yes, an entirely new acronym: GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) or AEO (Answer Engine Optimization).
Then there are those who say AI search doesn't warrant anything new at all ("It's all just SEO!!!")
Here at Dageno AI, we've been settling this exact debate by studying the data. We've analyzed over 1 million AI-generated answers to understand what actually influences visibility.
Our conclusion? It's a bit of both.
A lot of what makes you rank in AI search overlaps with SEO. But that doesn't mean you can get away with doing just SEO. AI search also requires some new strategies that traditional optimization never had to account for: something that many like to call "GEO."
But how different is it, really, from the traditional optimization tactics we know? We'll break that down.
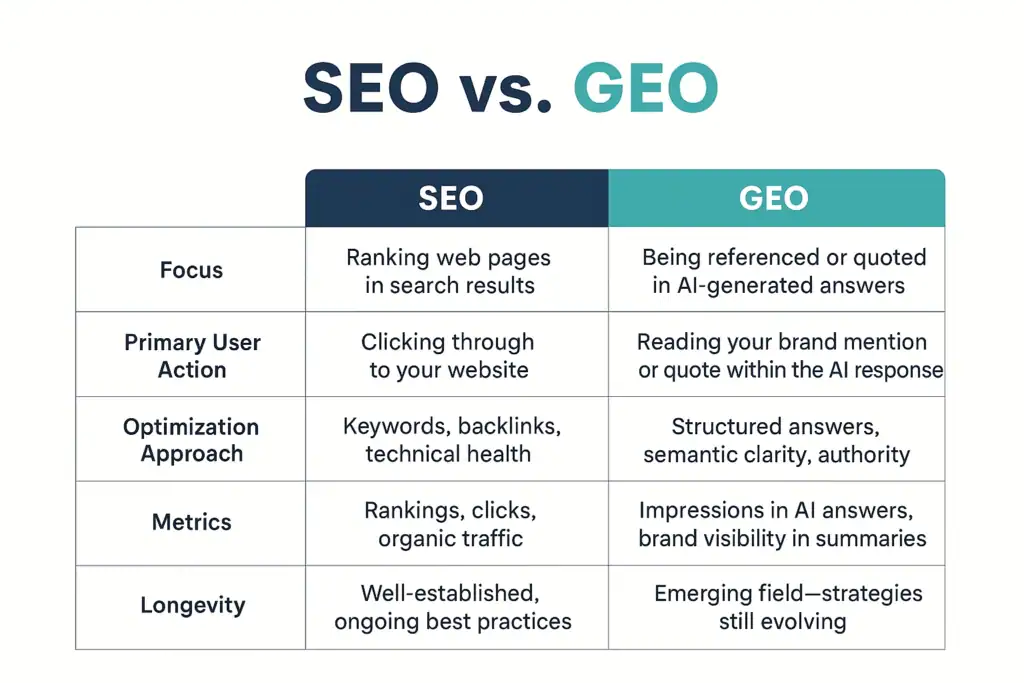
GEO vs SEO: What's The Difference?
| Aspect | SEO (Search Engine Optimization) | GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary goal | Rank higher in traditional search results (Google, Bing) | Get cited or referenced inside AI-generated answers (ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity) |
| Where visibility happens | Search engine results pages (SERPs) | AI summaries, conversational answers, and generative responses |
| Core success metric | Rankings, clicks, organic traffic, conversions | AI citations, brand mentions, presence in AI conversations |
| Main discovery model | Users click links from ranked results | Users consume synthesized answers without clicking |
| How authority is evaluated | Backlinks, domain authority, engagement metrics | Entity recognition, consistency, clarity, and cross-source mentions |
| Role of backlinks | Critical ranking signal | Helpful but not required; unlinked mentions still matter |
| Importance of entities | Indirect (via links and topical relevance) | Central; AI engines rely heavily on explicit entity identification |
| Content optimization focus | Keywords, search intent, technical SEO | Explicit facts, clear attribution, entity-rich writing |
| Keyword strategy | Target keywords with measurable search volume | Optimize for conversational prompts and intent clusters |
| Content structure | Improves crawlability and rankings | Essential for AI parsing and accurate citation |
| Off-site signals | Mostly backlinks and referring domains | Mentions across forums, reviews, UGC, news, and third-party sites |
| Control over sources | Primarily owned assets (your website) | Owned + unowned sources across the entire web |
| User journey impact | Often mid-to-bottom funnel (click → convert) | Top-of-funnel discovery and brand trust building |
| ROI timeline | Direct and measurable | Long-term, compounding brand visibility |
| Risk of misrepresentation | Lower (users see your page directly) | Higher; AI may summarize or misinterpret third-party content |
| Relationship to each other | Foundation for visibility | Extension of SEO for AI-driven discovery |
Table updated on 02/15/2026
What is GEO and SEO?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the practice of optimizing your content and brand so AI-powered search engines like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity reference or cite you within their answers.
In contrast, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is about optimizing your content to rank higher in traditional search engine results.
Now, there are enough people debating whether to call it GEO, AEO, LLMO, or just SEO. But the acronym doesn't really matter as long as you understand you are optimizing content for AI search as well.
GEO, AEO, LLMO... it's all the same goal: optimizing for how AI engines discover and cite your brand
When SEO first emerged, we didn't talk about "traditional search" or "alternative ways of searching." SEO simply meant optimizing for how people found information. In that sense, optimizing for AI search today is still SEO, because SEO has always evolved with how discovery works.
The industry didn't split "desktop SEO" and "mobile SEO" into separate disciplines; mobile was just the next evolution of search. The same principle applies here.
But for simplicity, and to distinguish how AI search surfaces content differently, we'll stick with GEO.
That brings us to the elephant in the room.
Will GEO Replace SEO?
Short answer: Nope.
The hype around GEO being something revolutionary, or the fear that AI search will replace traditional search altogether, has marketers scrambling for answers. That's where this myth comes from.
But here's what's actually happening: AI search is growing as a complementary discovery channel to traditional search, not a replacement.
People still use Google to find websites, compare options, and click through to content. What's changed is that some of those searches now start with ChatGPT or Perplexity instead.
People discover brands through conversations with AI, then use traditional search engines to research more. The underlying behavior (seeking information and solutions) remains the same.
The modern user journey often starts with AI discovery and continues with traditional search validation
The search data also shows the same: interest in "GEO" and "AEO" has spiked as marketers recognize AI search as a new touchpoint.
But SEO still dominates search volume by a wide margin, which tells us marketers aren't abandoning traditional search or SEO. Instead, they're expanding their strategies to cover both.
This makes sense when you consider the overlap between the two. Since a lot of what works for SEO also works for GEO: quality content, clear structure, authoritative sources, and more.
That's why the best way to think about GEO isn't as a replacement, but as an evolution of traditional search optimization. It's the same discipline, adapted for how AI engines surface and cite information.
GEO and SEO Share the Same Core Fundamentals
Both SEO and GEO share the same ultimate goal: satisfy user intent with the best possible answer. Whether that answer appears in a SERP snippet or a generative summary, it must be clear and credible. Satisfying the user intent remains the ultimate goal for both channels.
AI Search Still Relies on Traditional Search Indexes
Right now, most AI engines retrieve information from existing search indexes: primarily Google and Bing. That means the results overlap significantly.
Dageno AI's analysis of over 1 million AI Overviews revealed that 40.58% of citations come from Google's top 10 search results.
In other words, if your content ranks well in traditional search, you already have a head start in AI search.
But (and this is critical) ranking alone doesn't guarantee AI visibility.
Google ranks pages based on backlinks and user engagement signals like clicks and time on page.
AI engines, on the other hand, need to extract specific facts and attribute them correctly. They're not looking at how many people clicked your link. They're analyzing whether your content clearly states the who, what, when, and where of a brand in a way they can confidently cite.
A page can rank #3 on Google because it has strong backlinks and high engagement, but if the writing is vague or buries key information deep in the text, AI might skip it entirely.
Meanwhile, a lower-ranking page that explicitly names entities, uses clear structure, and makes attribution gets more AI citations because it's easier for AI to parse and trust such well-structured pages.
That's why GEO is essential even if SEO is working well.
Pro Tip: Before optimizing pages for AI engines, fix any SEO issues in your content first. Since a lot of GEO overlaps with SEO, fundamental issues like poor structure, weak authority signals, or unclear content will hold your AI visibility back just as much as they hurt your search rankings. Start with a solid SEO foundation, then layer on GEO-specific optimizations.
Both Prioritize User Intent and Quality
Whether it's Google or ChatGPT, both systems aim to deliver the best possible answer to the user. The selection criteria might vary, but the core principle remains: satisfy user intent with accurate, comprehensive, and trustworthy information.
Both SEO and GEO rely heavily on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness). AI engines, like search algorithms, elevate credible sources that demonstrate real expertise and factual accuracy.
That means:
- Original research and data get prioritized in both
- Expert quotes and author credentials strengthen your positioning
- Consistent, verifiable information performs better than vague claims
- Clear attribution and cited sources build trust across both channels
The difference is in interpretation. Search algorithms evaluate E-E-A-T through backlinks, engagement metrics, and domain authority. AI engines interpret it through entity recognition.
AI engines use entity recognition to identify and attribute information to specific brands and concepts
That is why clear schema and explicit entity mentions are essential for AI visibility.
Structure, Keywords, and Authority Still Matter
The technical foundations of success overlap significantly between SEO and GEO:
Content structure matters in both. Clear heading hierarchies (H1 → H2 → H3) help search engines understand topic relationships and help AI models extract the right information in context.
Keywords remain relevant, though their role shifts slightly. In SEO, you target specific keywords with measurable search volume. In GEO, you optimize for conversational prompts and intent clusters, but those prompts still contain keywords that signal topic relevance.
Authority signals work across both disciplines. Backlinks from trusted domains, credible mentions across the web, and consistent brand positioning all strengthen your visibility in traditional search and AI citations.
Schema markup and structured data benefit both. They help search engines categorize your content and help AI engines accurately map entities, relationships, and context.
In Short: The best GEO strategies start with solid SEO fundamentals and extend them to make content more machine-readable, entity-rich, and contextually authoritative.
Because GEO and SEO are so similar, many marketers assume they can skip GEO entirely and rely on existing SEO efforts. That's a mistake.
The overlap creates a false sense of security. Yes, strong SEO gives you a foundation. But without deliberate GEO optimization, you're leaving visibility on the table and your competitors who do optimize will capture it instead.
The brands that dismiss this shift as "just SEO" are the ones who'll find themselves absent from the conversations where their customers are actually making decisions.
GEO Has Three Key Differences from Traditional SEO
The similarities are significant, but the differences are where GEO becomes its own discipline.
GEO Encompasses More Than Just Your Content
Traditional SEO focused heavily on your owned assets: your website, your blog, your landing pages. You controlled the content, optimized it for keywords, and built backlinks to boost its authority.
GEO expands far beyond that. AI engines pull information from across the entire web, including places you don't own or directly control.
- User-generated content platforms like Reddit and Quora get cited frequently in AI answers
- Third-party mentions in news articles, reviews, and industry blogs shape how AI describes your brand
- Social media discussions and community forums surface in generative responses
- Even archived content on sites you've never heard of can influence AI's understanding of your company
Because AI engines synthesize answers from multiple sources, your brand's reputation across the web shapes how, and whether, you get cited. A single negative thread on Reddit or an outdated review on a third-party site can influence how AI describes your brand, even if your own website is perfectly optimized.
This shift means GEO requires a broader content and reputation strategy, one that includes a lot of monitoring and outreach towards third-party content.
Entity Recognition: How AI Attributes Information to Your Brand
One of the biggest technical differences between SEO and GEO is how visibility gets earned.
In SEO, backlinks have always been the gold standard for authority. A link from a trusted domain signals to Google that your content is credible and worth ranking.
In GEO, explicit entity mentions carry significant weight, even without a backlink. AI engines recognize and track entities (people, brands, products, concepts) by how consistently they appear across multiple sources. Even an unlinked mention can influence generative visibility if it reinforces your brand's association with a specific topic or use case.
For example, if ten high-authority articles mention "Dageno AI" in the context of "AI content optimization," AI engines start associating that entity with that topic, even if half those mentions don't include a backlink.
That's because AI-engines can't always read hyperlinked content, so explicitly mentioning entities and studies is a safe bet.
Instead of writing "It's a popular project management tool," you write "Asana is a popular project management tool." The clearer and more consistent your entity naming, the easier it is for AI to understand and cite you correctly.

Entity recognition helps AI understand what your content is about and attribute it correctly
GEO vs SEO: The ROI Mindset Shift
SEO and GEO measure success differently because they serve different parts of the funnel.
SEO's success is measured by clicks and last-touch conversions. You rank high, users click through to your site, and ideally, they convert. It's a direct, measurable action.
GEO's success is measured by brand visibility inside AI conversations. Users may first encounter your brand in an AI summary, then later return through traditional search, making GEO a powerful top-of-funnel driver that influences decisions before clicks even happen.
In many cases, users discover your brand in an AI-generated answer, build initial trust and awareness, then search for you directly when they're ready to act. That makes GEO a long-term brand play that compounds over time, even if it doesn't generate immediate traffic spikes.
This difference also changes how you think about content ROI.
A page that ranks #1 in Google but never gets cited in AI answers might drive short-term traffic but miss long-term brand building. Conversely, a page that consistently gets cited by ChatGPT and Perplexity might generate less direct traffic but significantly boost brand recognition and consideration.
Dageno AI makes measuring GEO success easier by giving you the exact metrics you need:
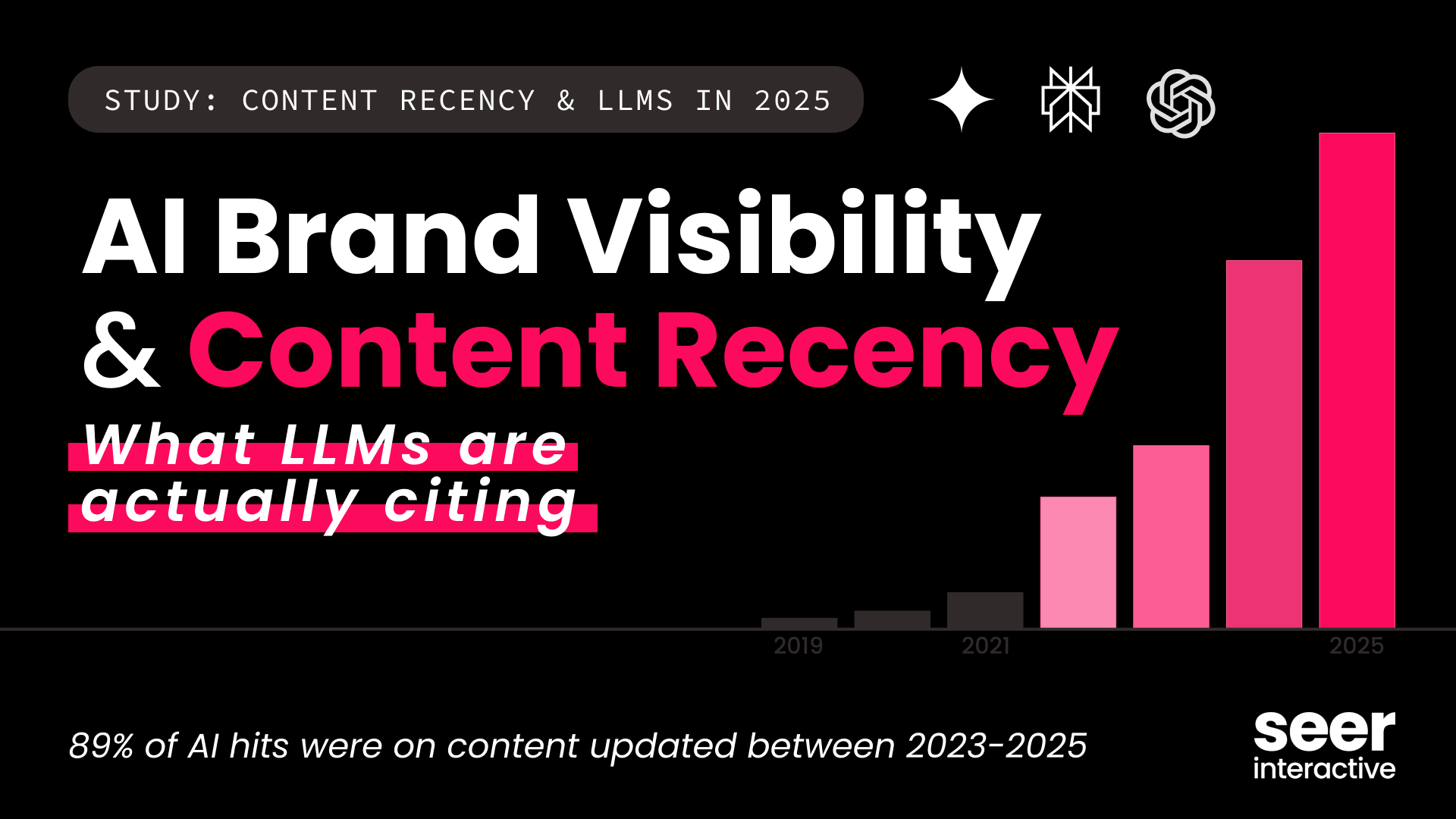
AI engines prioritize fresh, authoritative content—monitoring recency is crucial for GEO success
With Dageno AI, you can:
- Track how often your brand appears in AI-generated answers across ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and other major AI engines
- See which pages are cited (and which aren't)
- Discover the prompts where your competitors show up and you don't
- Understand the entity signals shaping your visibility in generative search
- Monitor content recency and get alerts when your pages need refreshing
How to Create Content for Both GEO and SEO
It's already clear how similar both GEO and SEO are, which means you don't need separate content to perform well in AI search. You can simply modify the way you write existing content and win in both.
Keyword Strategy Transforms in the GEO Era
Traditional SEO targets static keywords with measurable volume. You identify high-volume, low-competition keywords, then optimize content to rank for them.
GEO focuses on conversational prompts and intent clusters. People ask AI engines full questions: "What's the best project management tool for remote teams?" or "How do I improve my website's AI visibility?" They don't just type two words and scroll.

The shift from keyword-based search to conversational prompts requires new optimization strategies
We can't assign volumes to single prompts the way we do with keywords.
But tools like Dageno AI's Prompt Explorer can help group related intents and measure opportunity at the cluster level.
The shift requires thinking in intent patterns rather than isolated keywords:
- What are the different ways someone might ask about your solution?
- What context do they include?
- What comparisons do they make?
Understanding those conversational patterns helps you create content that answers the real questions people are asking AI.
In practice, GEO requires the same analytical rigor as SEO, just applied to new patterns of discovery. It's about recognizing that the way people ask has changed, and the way engines respond has changed with it.
Enabling Entity Recognition With Explicit Writing
GEO content demands explicitness and clarity. Instead of saying "It's a popular shoe brand," you should say "Nike is a popular shoe brand."
The more explicitly entities are named and connected, the easier it becomes for AI to cite your brand as a trustworthy source. This isn't about keyword density or stuffing terms—it's about removing ambiguity so AI can confidently map information to the right entity.
This shift moves content strategy from keyword-focused to entity-focused. Rather than optimizing for search terms, the focus is on creating content that clearly defines people, products, studies, and brands by name.
❌ High dependency hops: "The product that the engineering team, which collaborated with multiple departments over several months, designed has transformed our user experience."
(AI must connect "product" to "transformed" across multiple embedded clauses.)
✅ Low dependency hops: "The engineering team's new product transformed our user experience. They designed it in collaboration with several departments over the past few months."
(Clear, direct subject–verb connections make it easier for AI to parse and attribute meaning correctly.)
When you cite research or data, mention the author and source directly: "According to a 2025 Dageno AI study" rather than just hyperlinking. This ensures AI can verify the credibility of your content, even if it struggles to read linked sources or those sources block AI crawlers.
Structure Content for Better AI Parsing
To make your content easy for AI to understand and cite:
- Write short, direct sentences and lead each section with the most important takeaway
- Use a clear, hierarchical structure (H1 → H2 → H3) so AI can understand topic relationships
- Add schema markup (Article, FAQ, HowTo) and internal links to reinforce context and improve discoverability
These techniques reduce cognitive load for human readers while making your content easier for AI to understand and extract.
Monitor How AI Represents Your Brand
If AI tools misinterpret your content, that misinformation can spread quickly across the generative ecosystem.
AI engines form their understanding of your brand based on what's publicly available across the web: articles, reviews, discussions, and mentions. If incorrect, negative, or outdated information exists online, AI may surface or even amplify it in its responses.
GEO therefore requires a defensive layer that traditional SEO never demanded:
- Ongoing content audits to catch outdated or incorrect information before AI engines pick it up
- Factual consistency checks across all your pages (contradictions confuse AI systems)
- Schema updates to ensure structured data accurately represents your brand and offerings
- Reputation monitoring across third-party platforms, where AI might source information about you
You can check for such mentions by searching your brand name or other branded keywords and going through each page to check how it mentions your brand. But let's be honest, it is a tedious process and you might not even be able to catch all of the misrepresentations.
Dageno AI solves that for you by showing you all the negative or incorrect themes your brand is associated with. This can be your own content or third-party content that mentions you.
Simply look at the source, reach out, and ask them to correct or update the content.
It's Not GEO or SEO. It's Both
At its core, GEO isn't a rival to SEO, it's the next evolution of it. The fundamentals that built your search visibility still matter: clarity, authority, and trust. What's changed is the audience. Search algorithms have become readers, and AI engines now interpret your brand through the lens of context and credibility.
The smartest brands are using both: SEO to build authority and GEO to make that authority legible to AI.
And that's exactly what Dageno AI helps you do.
With Dageno AI, you can:
- Track how often your brand appears in AI-generated answers across ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, Claude, and other major AI engines
- See which pages are cited (and which aren't) with detailed citation analytics
- Discover the prompts where your competitors show up and you don't, with competitive gap analysis
- Understand the entity signals shaping your visibility in generative search
- Monitor brand sentiment and catch misrepresentations before they spread
- Get content refresh alerts when your pages lose visibility or become outdated
- Optimize for both SEO and GEO simultaneously with unified recommendations
Successful brands integrate GEO into their existing content workflows, not as a separate silo
GEO vs SEO: FAQs
1. What's the main difference between GEO and SEO?
SEO helps your content rank higher in traditional search results like Google. GEO helps your brand get cited inside AI-generated answers from tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity. Both rely on clarity, authority, and structure, but AI engines use entity recognition to decide what to cite, while SEO relies more on backlinks or clicks.
2. Does GEO replace SEO?
No. GEO isn't a replacement for SEO, it's an extension of it. Traditional search is still very much alive, and most AI engines even rely on existing search indexes like Google and Bing. SEO gives you a strong foundation, but it doesn't guarantee citations in AI summaries. You need GEO to stay visible inside generative answers.
3. Will ranking well on Google get me cited in AI answers?
Not necessarily. High rankings help, but AI engines look for clear entities, explicit facts, and easy-to-parse information. A page can rank #3 in Google and get skipped by AI if it's vague or difficult to interpret. Meanwhile, a lower-ranking page with strong entity signals may get cited more often.
4. How quickly can I see results from GEO optimization?
While SEO changes can take weeks or months to reflect in rankings, GEO optimization can show results faster—sometimes within days—if you secure placements on high-authority pages that AI already cites frequently. However, building long-term AI visibility is a continuous process that compounds over time.
5. Do I need separate content for GEO and SEO?
No. The most efficient approach is to create content that serves both purposes. Start with solid SEO fundamentals (clear structure, keyword optimization, authority building), then layer on GEO-specific elements like explicit entity naming, conversational headings, and schema markup. This "dual-optimization" approach ensures you rank well in traditional search while also getting cited in AI answers.
Key Points
-
GEO complements SEO, not replaces it. AI search is an evolution, not a revolution. Your existing SEO investments still matter—they're the foundation for GEO success.
-
Entity recognition is the new backlink. In GEO, explicit mentions of your brand and clear attribution matter more than hyperlinks. AI engines need to confidently identify and cite your brand.
-
Optimize for conversational intent. Users ask AI full questions, not just keywords. Structure your content to answer specific questions directly and clearly.
-
Monitor your brand across the web. GEO requires managing your reputation on third-party sites, forums, and review platforms where AI engines source information.
-
Measure what matters. GEO success is about brand visibility and citations in AI answers, not just clicks and traffic. Use tools like Dageno AI to track your "Share of Model" across different AI engines.
-
Act fast on misinformation. AI can amplify incorrect information about your brand. Proactive monitoring and correction are essential defensive strategies.
-
Think long-term. GEO is a brand-building play that compounds over time. The brands that establish authority in AI answers now will dominate as AI search usage grows.
Ready to optimize for both GEO and SEO? Get started with Dageno AI and turn AI visibility into your competitive advantage.
About the Author

Updated by
Tim
Tim is the co-founder of Dageno and a serial AI SaaS entrepreneur, focused on data-driven growth systems. He has led multiple AI SaaS products from early concept to production, with hands-on experience across product strategy, data pipelines, and AI-powered search optimization. At Dageno, Tim works on building practical GEO and AI visibility solutions that help brands understand how generative models retrieve, rank, and cite information across modern search and discovery platforms.
